Ranking of β2 Adrenergic Receptor Agonists and Antagonists
Using a Cell-Based GPCR Signaling Application
Chandrasekaran Vasudevan and Jeffrey R. Haskins
Abstract
G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR) signaling has great
importance in physiological development and various biological
processes and hence has become a significant focus for various
therapeutic groups in the area of drug discovery. As many of the
various GPCR signaling pathways have been well characterized,
a large number of chemical libraries are being synthesized
targeting the various GPCRs either as agonists or antagonists.
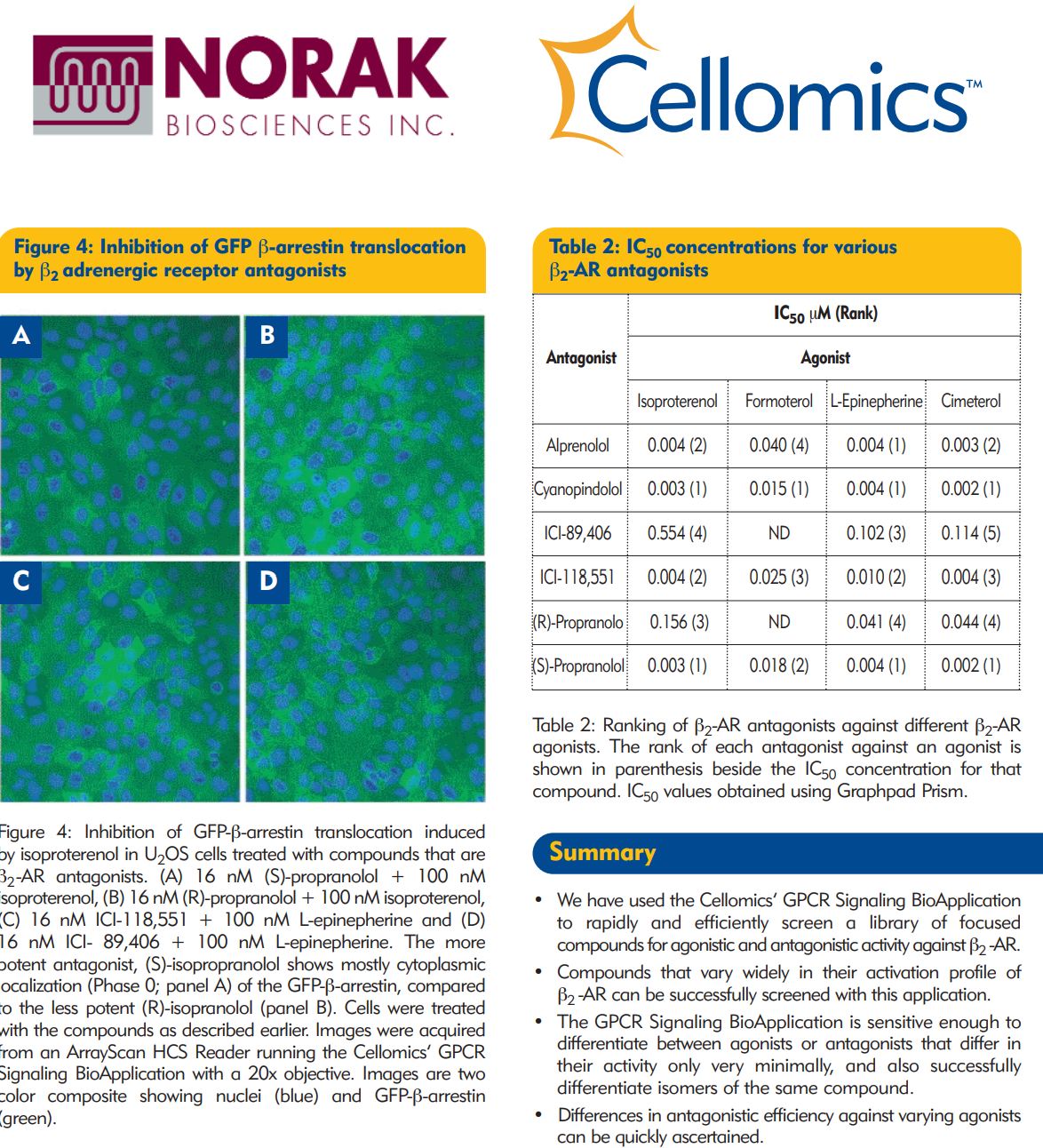
These compounds are usually ranked for potency against a
specific GPCR based on homogeneous biochemical assays. The
β2 adrenergic receptor (β2-AR) is a member of the GPCR family
of receptors, linked to adenylyl cyclase. The activation of β2-AR
is regulated by the binding of β-arrestins to the phosphorylated
receptor, leading to the internalization of the receptor. Cellomics
Inc., has developed a cell based high content screening, GPCR
Signaling BioApplication for the ArrayScan® HCS Reader that
uses Norak’s Transfluor™ technology and allows for the screening
of compounds that affect the GPCR signaling cascade. This
application quantitates GPCR activation by measuring
translocation of a GPCR activated β2-arrestin-GFP chimera in